乳腺超声读片不同于传统的放射学读片,需要通过超声医师自己直接操作,获得病变的超声影像,并且经过观察、分析、鉴别和判断,最后获得准确的超声诊断,因此高度依赖于超声医师个人的经验。此外,虽然现代数字化影像存档和通信系统能够存储超声影像片段可供全面重新读片,但是超声检查期间对病变进行实时分析仍然不可替代。计算机辅助实时影像分析可能有助于解决这些问题。
2024年9月10日,北美放射学会(RSNA)官方期刊《放射学》在线发表德国亚琛理工大学、弗劳恩霍夫数字医学研究所的研究报告,将经典放射组学结合自动化编码实现自动定位病变特征,能够根据超声影像精准实时区分良性与恶性乳腺肿瘤。
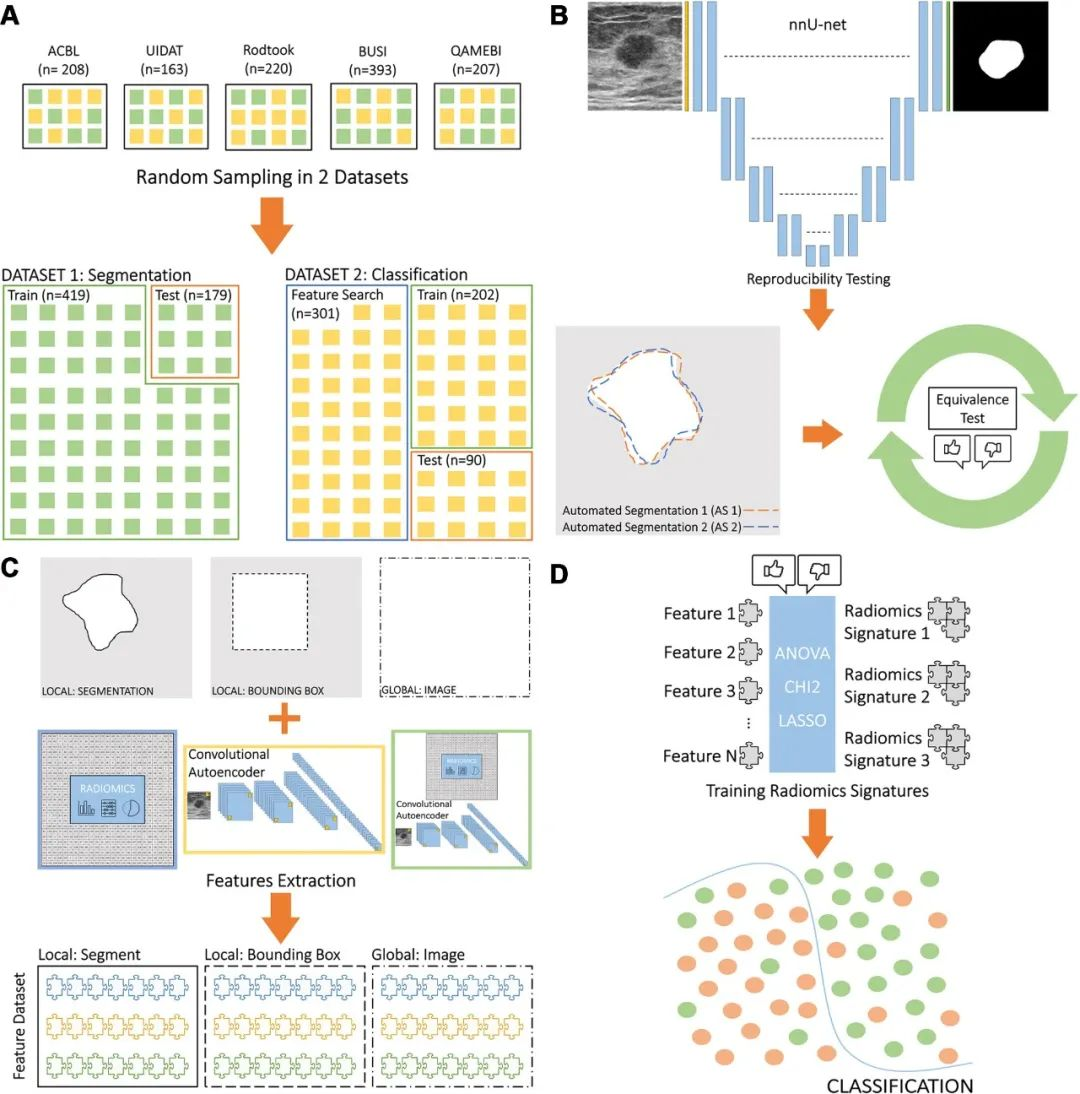
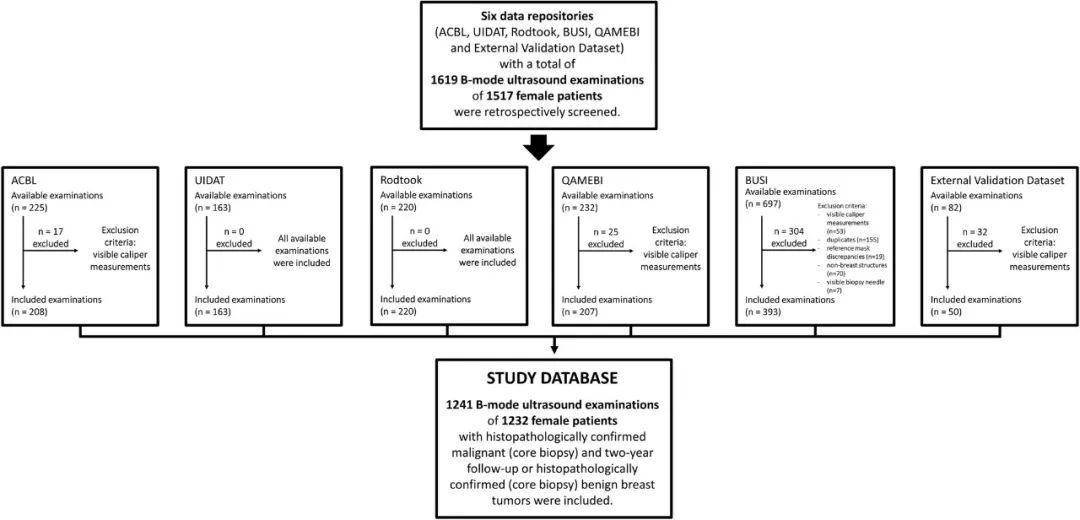
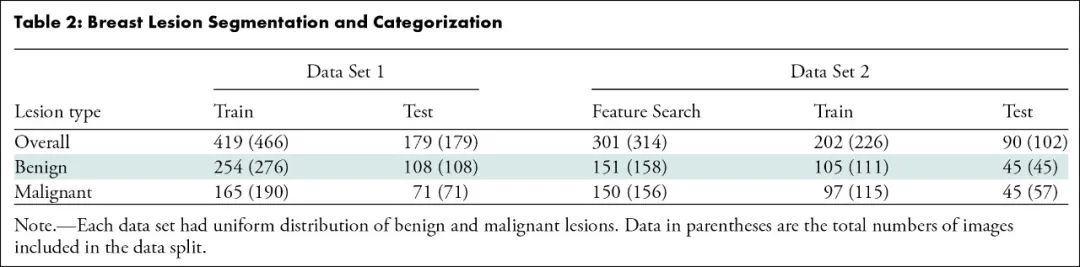
该研究首先对2018年4月至2024年1月ACBL、UIDAT、Rodtook、BUSI、QAMEBI以及外部数据库1517例女性患者的1619次乳腺肿瘤B超检查影像进行回顾分析,随后筛选出其中1182例(平均年龄61±14岁)女性患者的1191次乳腺肿瘤B超检查影像及其粗针活检组织病理学检查结果以及2年随访数据,利用人工智能深度学习三维生物医学影像分割方法进行病变分割训练,利用经典放射组学、自动化编码或两者从肿瘤段、边界框和整个影像提取特征,进行特征选择以生成放射组学特征,训练用于肿瘤分类的人工智能机器学习算法模型。建模数据集被分为两部分:测试和训练病变分割(419次和179次检查)和病变分类(503次和90次检查)。根据真假阳性率曲线下面积、灵敏度(真阳性率)和特异度(真阴性率)对模型进行评估,并与粗针活检组织病理学检查结果或者2年随访确认的诊断进行统计学比较。最后,对50例(平均年龄55±15岁)患者进行外部验证。
结果,该模型对测试数据集病变分割的精确度和可重复性极高:
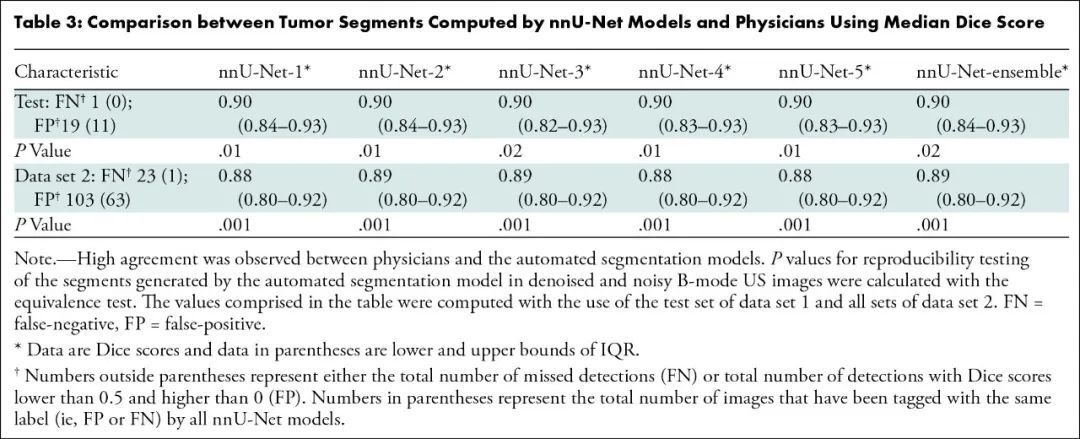
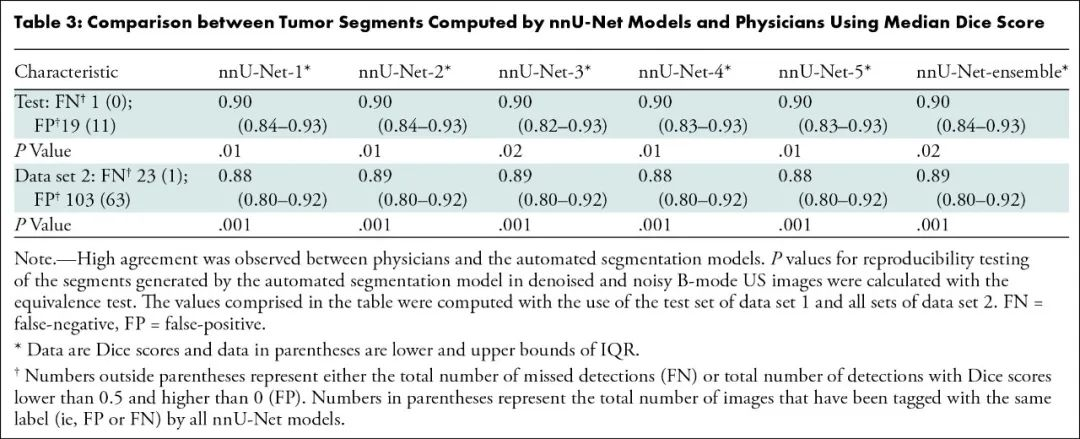
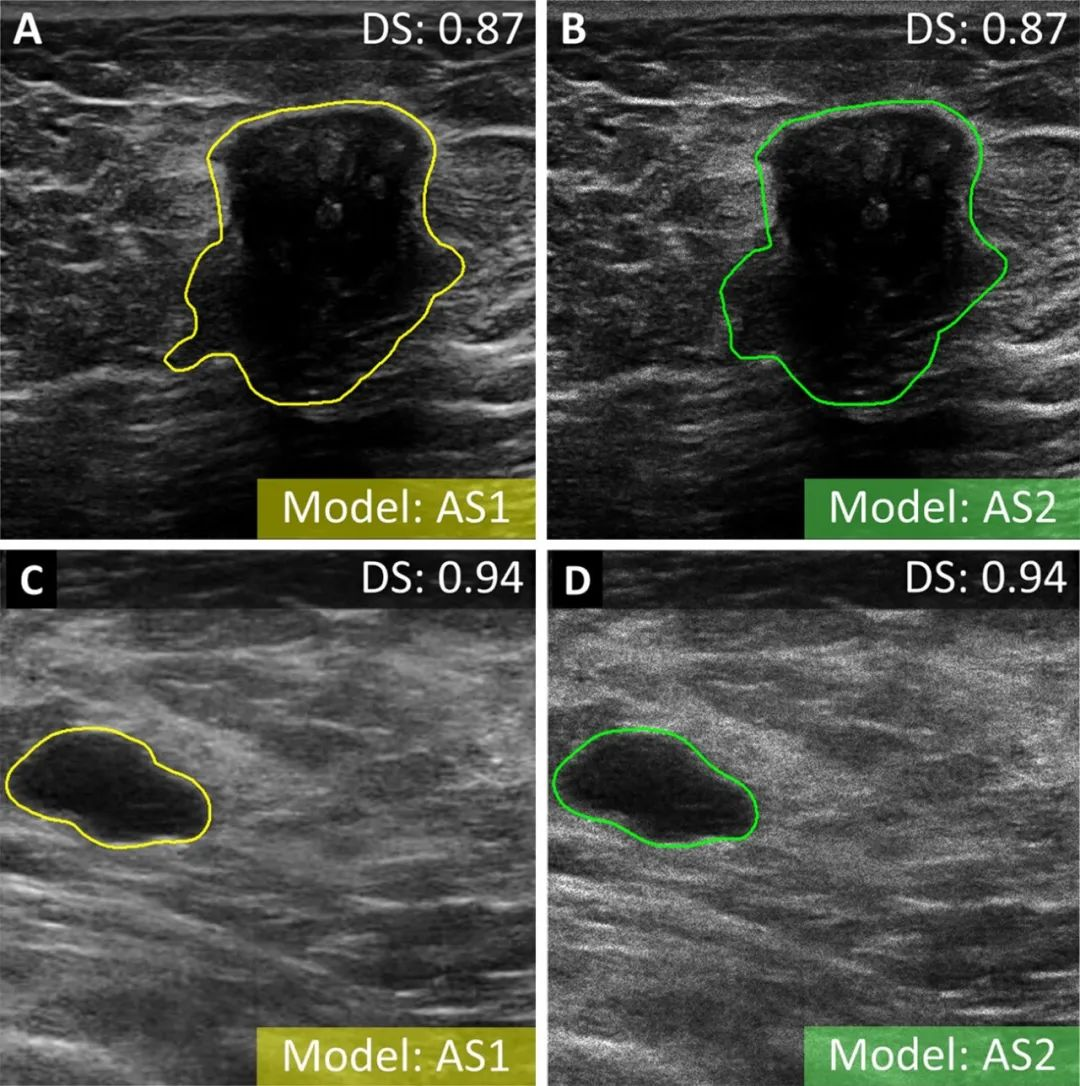
利用肿瘤边界框23个混合特征进行训练的肿瘤分类模型最精准:
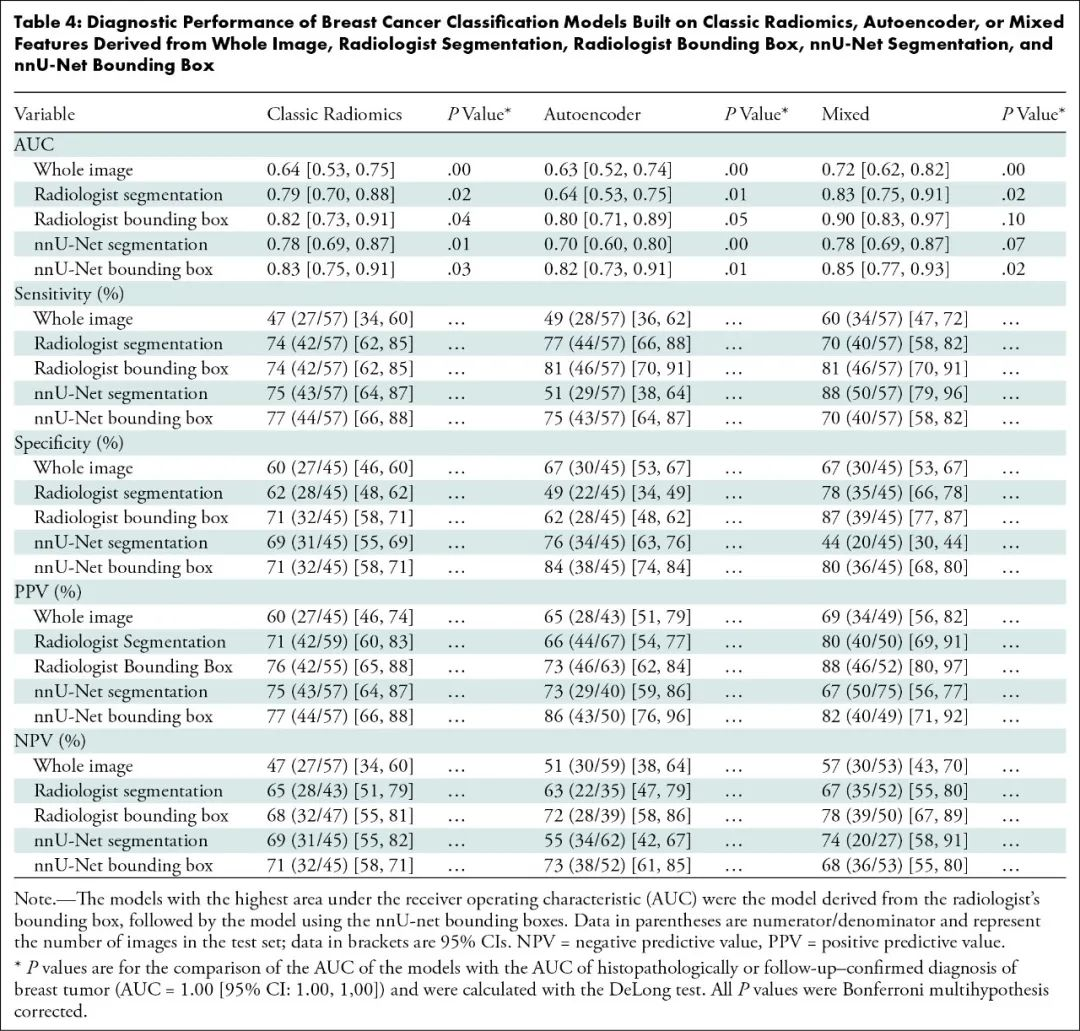
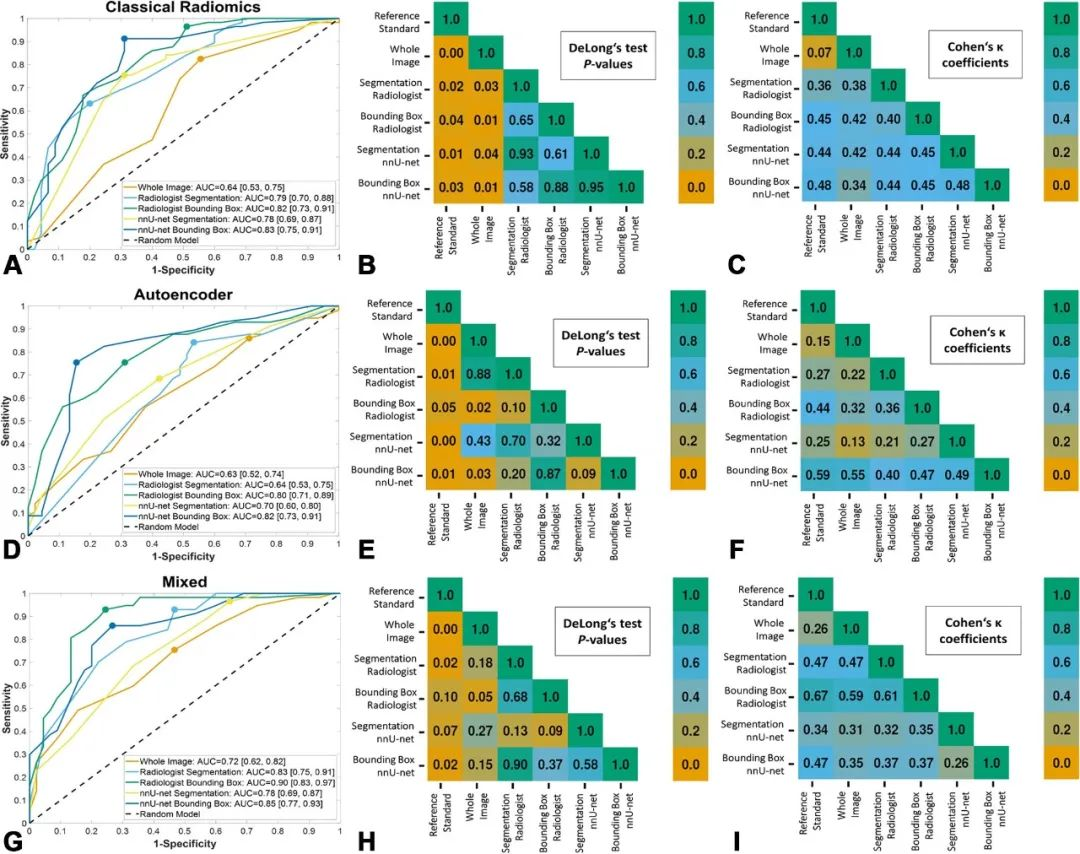
该模型与拥有3年和20年乳腺超声检查经验的2位读片者相比,肿瘤分类真假阳性率曲线下面积相似:
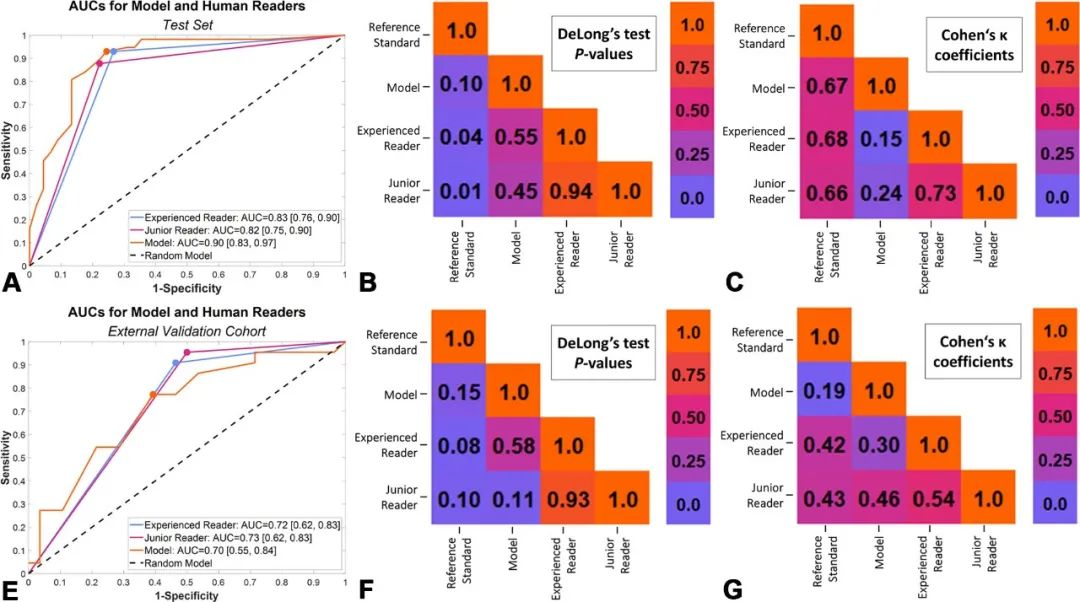
该模型与粗针活检组织病理学检查结果或者2年随访确认的诊断相比,曲线下面积相似:0.90比1.00(95%置信区间:0.83~0.97、1.00~1.00;P=0.10)。
因此,该研究结果表明,利用经典放射组学结合自动化编码的肿瘤边界框特征,可以根据超声影像对乳腺肿瘤实现精准实时分类,略胜拥有多年乳腺超声检查经验的人类读片者,接近粗针活检组织病理学检查结果或者2年随访确认的诊断。
对此,美国哈佛大学麻省总医院发表同期评论:人工智能结合放射组学提高乳腺超声检查准确性。
Radiology. 2024 Sep 10;312(3):e232554. IF: 12.1
Combining Radiomics and Autoencoders to Distinguish Benign and Malignant Breast Tumors on Ultrasound Images.
Magnuska ZA, Roy R, Palmowski M, Kohlen M, Winkler BS, Pfeil T, Boor P, Schulz V, Krauss K, Stickeler E, Kiessling F.
RWTH Aachen University, Aachen, Germany; Comprehensive Diagnostic Center Aachen, Uniklinik RWTH Aachen, Aachen, Germany; Fraunhofer Institute for Digital Medicine MEVIS, Bremen, Germany.
BACKGROUND: Ultrasound is clinically established for breast imaging, but its diagnostic performance depends on operator experience. Computer-assisted (real-time) image analysis may help in overcoming this limitation.
PURPOSE: To develop precise real-time-capable ultrasound-based breast tumor categorization by combining classic radiomics and autoencoder-based features from automatically localized lesions.
MATERIALS AND METHODS: A total of 1619 B-mode ultrasound images of breast tumors were retrospectively analyzed between April 2018 and January 2024. nnU-Net was trained for lesion segmentation. Features were extracted from tumor segments, bounding boxes, and whole images using either classic radiomics, autoencoder, or both. Feature selection was performed to generate radiomics signatures, which were used to train machine learning algorithms for tumor categorization. Models were evaluated using the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC), sensitivity, and specificity and were statistically compared with histopathologically or follow-up-confirmed diagnosis.
RESULTS: The model was developed on 1191 (mean age, 61 years ± 14 [SD]) female patients and externally validated on 50 (mean age, 55 years ± 15]). The development data set was divided into two parts: testing and training lesion segmentation (419 and 179 examinations) and lesion categorization (503 and 90 examinations). nnU-Net demonstrated precision and reproducibility in lesion segmentation in test set of data set 1 (median Dice score [DS]: 0.90 [IQR, 0.84-0.93]; P = 0.01) and data set 2 (median DS: 0.89 [IQR, 0.80-0.92]; P = 0.001). The best model, trained with 23 mixed features from tumor bounding boxes, achieved an AUC of 0.90 (95% CI: 0.83, 0.97), sensitivity of 81% (46 of 57; 95% CI: 70, 91), and specificity of 87% (39 of 45; 95% CI: 77, 87). No evidence of difference was found between model and human readers (AUC = 0.90 [95% CI: 0.83, 0.97] vs 0.83 [95% CI: 0.76, 0.90]; P = 0.55 and 0.90 vs 0.82 [95% CI: 0.75, 0.90]; P = 0.45) in tumor classification or between model and histopathologically or follow-up-confirmed diagnosis (AUC = 0.90 [95% CI: 0.83, 0.97] vs 1.00 [95% CI: 1.00, 1.00]; P = 0.10).
CONCLUSION: Precise real-time ultrasound-based breast tumor categorization was developed by mixing classic radiomics and autoencoder-based features from tumor bounding boxes.
PMID: 39254446
DOI: 10.1148/radiol.232554
Radiology. 2024 Sep 10;312(3):e241795. IF: 12.1
Combining AI and Radiomics to Improve the Accuracy of Breast Ultrasound.
Bahl M.
Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, MA.
PMID: 39254454
DOI: 10.1148/radiol.241795
文章来源于“SIBCS”,作者“北美放射学会”

【开源免费】DeepBI是一款AI原生的数据分析平台。DeepBI充分利用大语言模型的能力来探索、查询、可视化和共享来自任何数据源的数据。用户可以使用DeepBI洞察数据并做出数据驱动的决策。
项目地址:https://github.com/DeepInsight-AI/DeepBI?tab=readme-ov-file
本地安装:https://www.deepbi.com/
【开源免费】airda(Air Data Agent)是面向数据分析的AI智能体,能够理解数据开发和数据分析需求、根据用户需要让数据可视化。
项目地址:https://github.com/hitsz-ids/airda