在人工智能快速发展的今天,大语言模型(LLM)已经成为改变世界的重要力量。然而,如何高效地编写、管理和维护提示词(Prompt)仍然是一个巨大的挑战。传统的提示词工程往往依赖于手工编写和维护大量的文本模板,这不仅效率低下,而且难以进行版本控制和复用。
APPL(A Prompt Programming Language)的出现,为这个问题提供了一个优雅而强大的解决方案。作为连接程序和大语言模型的桥梁,APPL允许在Python函数中无缝嵌入提示词,同时也支持将提示词转换为结构化的程序代码。这种双向转换能力让开发者能够充分利用两个世界的优势:程序的精确控制和大语言模型的灵活创造力。
APPL是一个扩展了Python的提示词编程语言,它提供了一种自然、直观、便捷且高效的方式来在程序中使用大语言模型。作为一个专门面向Prompt工程师的工具,APPL不仅简化了提示词的编写和管理过程,还引入了一系列创新性的特性,从根本上改变了我们与大语言模型交互的方式。
APPL的第一作者:董宏华博士,本科毕业于清华大学交叉信息研究院(姚班),目前是多伦多大学在读博士。他带领团队开发了这个创新性的工具。作为专注于大语言模型应用的研究者,他们团队深入理解了当前Prompt工程师在日常工作中面临的挑战,并将这些洞察融入到APPL的设计中。他希望通过APPL,能够为广大的Prompt工程师提供一个更加高效、专业的开发工具,使他们能够更好地发挥创造力,构建更加复杂和强大的AI应用。
注意:本文以下示例代码由董宏华博士亲自修订。
网页文档:https://appl-team.github.io/appl
上手教程:https://appl-team.github.io/appl/tutorials/
代码:https://github.com/appl-team/appl
论文:https://arxiv.org/abs/2406.13161
安装:
pip install -U applang
APPL的核心创新在于其提示词上下文(Prompt Context)系统。这个系统不仅仅是简单的文本管理,而是一个复杂的状态管理机制:
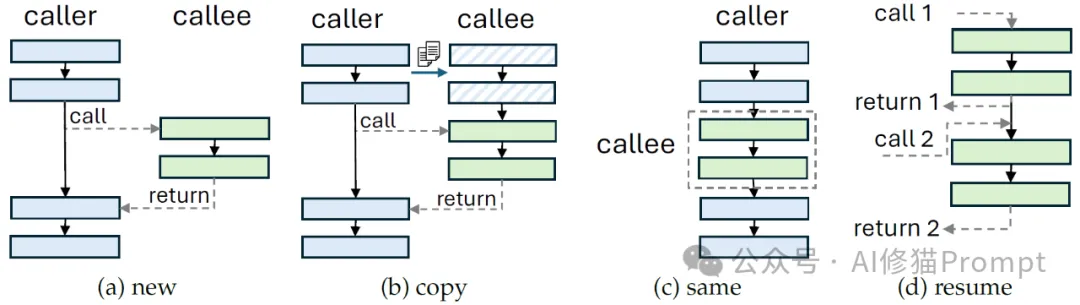
1.上下文生命周期管理
2.提示词捕获机制
3.上下文状态追踪
示例代码展示提示词的简洁用法:
from appl import ppl, gen
@ppl(docstring_as="system")
def simple_prompt(name: str):
"""This is a system prompt"""
f"Hello, my name is {name}!"
return gen()
simple_prompt("APPL")的提示词如下
system: This is a system prompt
user: Hello, my name is APPL
这被用于gen()函数来调用大语言模型。
示例代码展示上下文管理的高级用法:
import appl
from appl import SystemMessage, convo, ppl, gen
@ppl
def complex_prompt(data: dict, mode: str = "default"):
# 基础上下文设置
SystemMessage("Processing data analysis request")
# 条件性提示词构建
if mode == "detailed":
f"Analysis mode: Detailed examination"
f"Required aspects: All data fields"
else:
f"Analysis mode: Quick overview"
f"Required aspects: Key metrics"
# 动态数据注入
f"Input data summary:"
for key, value in data.items():
f"- {key}: {value}"
# 使用Python控制流动态构建提示词
if "errors" in data:
f"Special attention: Error analysis required"
f"Error details: {data['errors']}"
return convo() # convo即conversation,表示当前的对话提示词
print(complex_prompt({"name": "John", "age": 30, "errors": "Syntax error"}))
得到的输出如下:
system: Processing data analysis request
user: Analysis mode: Quick overview
Required aspects: Key metrics
Input data summary:
- name: John
- age: 30
- errors: Syntax error
Special attention: Error analysis required
Error details: Syntax error
APPL的并行化系统远比表面看到的要复杂。它实现了一个智能的任务调度器,能够自动识别和优化并行执行机会。在实际测试中,APPL展现出了显著的性能优势:
这些性能提升主要得益于以下技术实现:
除此之外,APPL还提供了以下高级特性:
高级并行处理示例:
@ppl
def parallel_processing(documents: list[str]):
SystemMessage("You are a document analysis tool.")
# 并行执行每个文档的分析任务
results = [analyze_document(doc) for doc in documents]
# 结果汇总
f"Analysis Summary:"
for doc_id, result in enumerate(results):
f"Document {doc_id}: {result}"
print(convo()) # DEBUG,打印用于生成(gen)的对话提示词
return gen()
@ppl(ctx="copy") # 使用独立的上下文副本
def analyze_document(doc: str):
"Analyze the following document:"
doc
return gen()
docs = ["first document ...", "second document ..."] # placeholder
print(f"\n=== Analysis Summary ===\n{parallel_processing(docs)}")
得到的输出如下:
system: You are a document analysis tool.
user: Analysis Summary:
Document 0: This document ... # (分析结果)
Document 1: This document ... # (分析结果)
=== Analysis Summary ===
These documents ... # (汇总的分析结果)
APPL的工具调用系统通过自动化的方式,将Python函数转换为大语言模型可以理解和使用的工具。这个过程包括:
1.函数签名分析
2.工具Schema生成
3.调用结果处理
这种自动化的工具集成机制大大简化了开发流程,使得开发者可以专注于业务逻辑的实现,而不需要手动处理繁琐的工具规范定义和参数转换。
示例代码:
# 常规的Python函数定义,参数类型可以是Pydantic模型
def is_lucky(x: int) -> bool:
"""Determine whether the input number is a lucky number.
Args:
x (int): The input number to be checked.
Returns:
bool: True if the number is a lucky number, False otherwise.
"""
return sympy.isprime(x + 3)
@ppl
def func(x):
f"Is {x} a lucky number?"
# 将 `is_lucky` 直接作为可用的工具,APPL会自动从函数签名和文档字符串中提取信息
# 结果是一个AssistantMessage,可以直接加入到提示词中
(actions := gen(tools=[is_lucky]))
if actions.is_tool_call: # LLM的选择是调用工具
# 运行工具,运行结果是ToolMessage的列表,可直接加入提示词中
(results := actions.run_tool_calls())
# results[0].content包含第一个工具调用的结果
# 让LLM根据结果生成文本答案,选择不使用工具
answer = gen(tools=[is_lucky], tool_choice="none")
else: # LLM选择直接生成答案
answer = actions.message
return answer
n = 2024
ans = func(n)
print("The answer is:", ans)
包含工具调用的对话的示例如下:
| Role | Message |
| -------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------- |
| User | Is 2024 a lucky number? |
| Assistant | [ToolCall(id='call_...', name='is_lucky', args='{"x":2024}')] |
| Tool(is_lucky) | True |
输出示例如下:
Yes, 2024 is a lucky number!
Tree of Thought(ToT)是一种强大的思维推理框架,它通过构建思维树并进行搜索来解决复杂问题。APPL为ToT提供了优雅而高效的实现支持,下面以24点游戏求解器为例展示APPL的强大能力:
@ppl
def propose(current_numbers: str):
f"Propose at most {args.n_propose_sample} possible next steps without explanation"
for example in PROPOSE_EXAMPLES:
for k, v in example.items():
display(k, v)
f"Input: {current_numbers}"
f"Possible next steps:"
return gen()
@ppl
def evaluate(current_numbers: str):
"Evaluate if given numbers can reach 24 (sure/likely/impossible)"
for example in VALUE_EXAMPLES:
for k, v in example.items():
display(k, v)
f"Input: {current_numbers}"
"Thoughts:"
return gen()
@traceable
def solve(input_numbers: str, steps: int = 3):
current_candidates = [
Game24Candidate(
start_numbers=input_numbers,
left_numbers=input_numbers,
steps=[]
)
]
for _ in range(steps):
# 生成可能的下一步
new_candidates = get_all_proposals(current_candidates)
# 评估每个候选解
new_candidates = get_all_values(new_candidates)
# 选择最佳候选解
current_candidates = sorted(
new_candidates,
key=lambda x: x.value,
reverse=True
)[: args.n_select_sample]
这个代码片段展示了APPL如何优雅地处理ToT的核心组件:
1.提案生成(propose):
2.评估(evaluate):
3.搜索(solve):
APPL的特性使得ToT实现具有以下优势:
在实际测试中,这个实现展现出了优秀的性能:
OPRO(Optimization of PROmpts)是谷歌DeepMind提出的一种创新的prompt优化技术,它通过迭代优化来提升prompt的效果,我之前有文章专门介绍过。
往期推荐
谷歌DeepMind重磅:提示工程师必须掌握OPRO,用LLM就能自动优化Prompt|ICLR2024
仅用十几行代码,APPL就能实现一个OPRO的简化版本,为类似算法提供了简洁而强大的实现支持:
@ppl
def optimize_prompt(question: str, prompt: str, output: str):
"I want to optimize the prompt for the question."
"The question is:"
question
"The current prompt is:"
prompt
"The output for the current prompt is:"
output
"The optimized prompt is:"
return gen()
@ppl
def evaluate_prompt(prompt: str):
prompt
return gen()
# 迭代优化过程
question = "Which number is larger, 9.11 or 9.9?"
prompt = "please think carefully."
for i in range(3):
# 评估当前prompt
output = evaluate_prompt(prompt)
# 生成优化后的prompt
prompt = optimize_prompt(question, prompt, output)
OPRO的工作原理:
1.初始prompt评估:
2.优化策略生成:
3.迭代优化过程:
APPL为OPRO提供的支持:
APPL特别适合实现基于ReAct范式的智能体系统,它能够自然地结合思考(Thought)、行动(Action)和观察(Observation):
@ppl
def react_agent(instruction: str, max_steps: int = 5):
SystemMessage("你是一个能够思考和使用工具的AI助手。")
f"用户指令: {instruction}\n"
tools = [finish_task]
for step in range(max_steps):
# 生成思考过程
f"思考: {gen(tools=tools, tool_choice='none')}"
# 选择并执行工具
(actions := gen(tools=tools))
# 运行并将结果加入提示词
(results := actions.run_tool_calls())
# 根据results判断是否完成任务,如果完成则退出循环
...
"生成最终答案:"
return gen()
这个实现展示了APPL如何优雅地处理复杂的交互流程,包括:
APPL可以方便地将整个文件夹内的代码放入提示词中,用于代码审查、讨论和调试。这种高级代码解析功能可以极大地提升开发效率,特别适用于代码审查、问题排查和团队协作:
以下代码展示了如何将文件目录结构与目录中代码以XML的格式放入提示词中,比如将APPL的examples作为source folder后,里面的所有代码都会进入提示词中,然后就可以跟这些示例进行交流。
@ppl
def chat(source_folder: str, ext: str = ".py"):
with Tagged("directory", attrs={"name": source_folder}):
"The source code is organized as follows:"
sd.seedir(
source_folder,
style="spaces",
printout=False,
exclude_folders=["__pycache__"],
)
with Tagged("source"):
"The contents of the source code are as follows:"
# 遍历目录下的所有文件
for name in glob.glob(
os.path.join(source_folder, "**", f"*{ext}"), recursive=True
):
with Tagged("file", attrs={"name": name}):
"```python"
with open(name, "r", encoding="utf-8") as f:
f.read() # 读取文件内容并放入提示词中
"```"
"Now begin the chat about the project:\n"
print(f"num_tokens: {get_num_tokens(str(convo()))}")
console = Console()
while True:
(query := prompt("User: ")) # 用户输入对话
if query.startswith("exit"):
break
console.print(make_panel(query, title="User"))
logger.info(f"User: {query}")
with AIRole():
(res := str(gen(stream=True).streaming(title="Assistant")))
logger.info(f"Assistant: {res}")
APPL作为一个开创性的提示词编程工具,展现出了显著的技术优势和广阔的应用前景:
1.架构设计:
2.开发体验:
3.性能优化:
1.开发效率:
2.应用场景:
3.生态潜力:
APPL代表了提示词工程的未来发展方向。它通过创新的技术架构和丰富的功能特性,为AI应用开发提供了一个强大而灵活的工具。对于Prompt工程师来说,掌握APPL不仅能够提高开发效率,还能够创造出更加强大和可维护的AI应用。
随着APPL的持续发展和完善,我们可以期待看到更多创新性的应用出现,推动整个AI领域向前发展。现在正是开始学习和使用APPL的最佳时机,让我们一起探索这个充满可能的新领域。
文章来自微信公众号“AI修猫Prompt”,作者“AI修猫Prompt”

【开源免费】Browser-use 是一个用户AI代理直接可以控制浏览器的工具。它能够让AI 自动执行浏览器中的各种任务,如比较价格、添加购物车、回复各种社交媒体等。
项目地址:https://github.com/browser-use/browser-use
【开源免费】AutoGPT是一个允许用户创建和运行智能体的(AI Agents)项目。用户创建的智能体能够自动执行各种任务,从而让AI有步骤的去解决实际问题。
项目地址:https://github.com/Significant-Gravitas/AutoGPT
【开源免费】MetaGPT是一个“软件开发公司”的智能体项目,只需要输入一句话的老板需求,MetaGPT即可输出用户故事 / 竞品分析 / 需求 / 数据结构 / APIs / 文件等软件开发的相关内容。MetaGPT内置了各种AI角色,包括产品经理 / 架构师 / 项目经理 / 工程师,MetaGPT提供了一个精心调配的软件公司研发全过程的SOP。
项目地址:https://github.com/geekan/MetaGPT/blob/main/docs/README_CN.md
【开源免费】LangGPT 是一个通过结构化和模板化的方法,编写高质量的AI提示词的开源项目。它可以让任何非专业的用户轻松创建高水平的提示词,进而高质量的帮助用户通过AI解决问题。
项目地址:https://github.com/langgptai/LangGPT/blob/main/README_zh.md
在线使用:https://kimi.moonshot.cn/kimiplus/conpg00t7lagbbsfqkq0